

Returns the Poisson cumulative distribution function at value x using the corresponding mean parameter in lambda.
#STANDARD NORMAL CDF CALCULATOR TRIAL#
The result y is the probability of observing up to x trials before a success, when the probability of success in any given trial is p.Ĭomputes the Negative binomial cumulative distribution at value x using the corresponding number of successes (R) and probability of success in a single trial (p). Ĭomputes a binomial cumulative distribution function at value x using the corresponding number of trials in N and probability of success for each trial in p.Ĭomputes a Geometric cumulative distribution where p is the probability of success, and x is the number of failures before the first success.

x x score so that the cumulative normal probability distribution is 0.89.
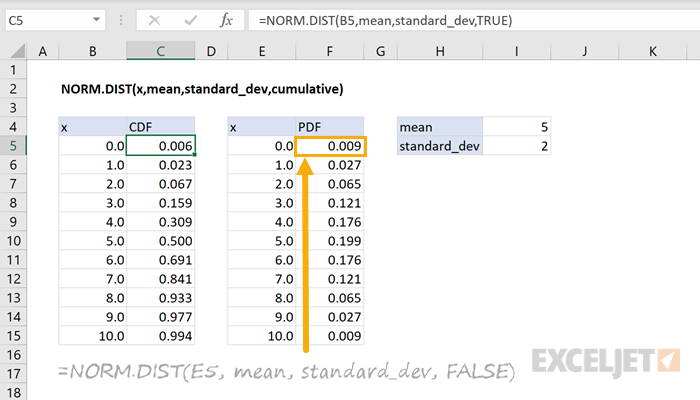
Example Codes : Calculating Random variates (rvs) of Distribution Using scipy. It implies the probability of occurrence of value less than or equal to 2 while sampling from a normal distribution with mean0 and standard deviation 1 is:0.977. Normal CDF calculator works based on the standard. More about this Inverse Cumulative Normal Probability Calculator. CDF Value of x2 in normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1 is :0.9772498680518208. The result p is the probability that a single observation from the t distribution with ν degrees of freedom will fall in the interval. Use our online Cumulative distribution function calculator for cumulative density function calculation. Returns the Gamma cumulative distribution function at value x using the corresponding shape parameters in a and scale parameters in b.Ĭomputes the Exponential cumulative distribution function at value x using the corresponding mean parameter µ.Ĭomputes a Student’s cumulative distribution function at value x where ν is the degrees of freedom and Γ( Returns values at x of the Lognormal cumulative distribution function with distribution parameters µ and σ, where µ and σ are the mean and standard deviation, respectively, of the associated normal distribution.Ī lognormal distribution with mean m and variance v has parameters µ and σ. The second parameter, σ, is the standard deviation. The normal distribution is a two-parameter family of curves. Returns the probability 'p' that a single observation from a Normal distribution with parameters µ and σ falls in the interval (-∞,x]. The discrete distributions are: Binomial, Geometric, Negative Binomial and Poisson. In this table, the continuous distributions are: Normal, Lognormal, Gamma, Exponential, and Student’s. and are the mean and standard deviation, respectively, of the associated normal distribution. The following table summarizes common continuous and discrete distributions, showing the cumulative function and its parameters. Practical Statistic Tools - Probability Calculator. The Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) is the probability that the random variable X will take a value less than or equal to x.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
